C++
C++入门及简单的顺序结构
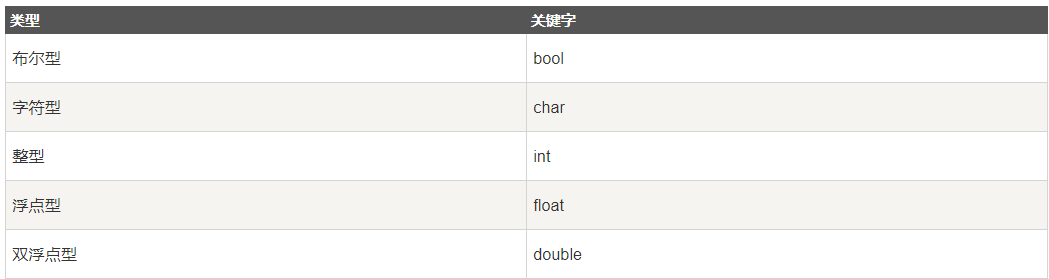
变量的定义
变量必须先定义,才可以使用。不能重名。
变量定义的方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int b, c = a, d = 10 / 2;
return 0;
}
|
常用变量类型及范围:
输入输出
整数的输入输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << a + b << endl;
return 0;
}
|
字符串的输入输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cin >> str;
cout << str;
return 0;
}
|
输入输出多个不同类型的变量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b;
string str;
cin >> a;
cin >> b >> str;
cout << str << " !!! " << a + b << endl;
return 0;
}
|
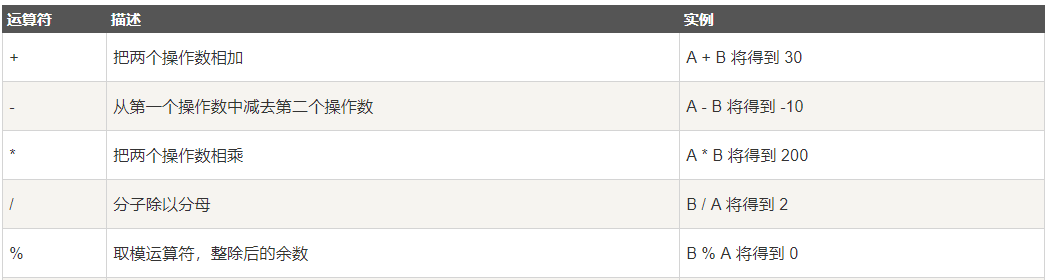
表达式
整数的加减乘除四则运算:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 6 + 3 * 4 / 2 - 2;
cout << a << endl;
int b = a * 10 + 5 / 2;
cout << b << endl;
cout << 23 * 56 - 78 / 3 << endl;
return 0;
}
|
浮点数(小数)的运算:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float x = 1.5, y = 3.2;
cout << x * y << ' ' << x + y << endl;
cout << x - y << ' ' << x / y << endl;
return 0;
}
|
整型变量的自增、自减:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 1;
int b = a ++ ;
cout << a << ' ' << b << endl;
int c = ++ a;
cout << a << ' ' << c << endl;
return 0;
}
|
变量的类型转换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float x = 123.12;
int y = (int)x;
cout << x << ' ' << y << endl;
return 0;
}
|
printf 语句与判断结构
printf 输出格式:
注意:使用 printf 时最好添加头文件 #include 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
printf("Hello World!");
return 0;
}
|
Int、float、double、char 等类型的输出格式:
- int:%d
- float: %f, 默认保留 6 位小数
- double: %lf, 默认保留 6 位小数
- char: %c, 回车也是一个字符,用’\n’表示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 3;
float b = 3.12345678;
double c = 3.12345678;
char d = 'y';
printf("%d\n", a);
printf("%f\n", b);
printf("%lf\n", c);
printf("%c\n", d);
return 0;
}
|
所有输出的变量均可包含在一个字符串中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 3;
float b = 3.12345678;
double c = 3.12345678;
char d = 'y';
printf("int a = %d, float b = %f\ndouble c = %lf, char d = %c\n", a, b, c, d);
return 0;
}
|
扩展功能:
float, double 等输出保留若干位小数时用:%.4f, %.3lf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float b = 3.12345678;
double c = 3.12345678;
printf("%.4f\n", b);
printf("%.3lf\n", c);
return 0;
}
|
最小数字宽度:
- %8.3f, 表示这个浮点数的最小宽度为 8,保留 3 位小数,当宽度不足时在前面补空格。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 3;
float b = 3.12345678;
double c = 3.12345678;
printf("%5d\n", a);
printf("%8.4f\n", b);
printf("%7.3lf\n", c);
return 0;
}
|
- %-8.3f,表示最小宽度为 8,保留 3 位小数,当宽度不足时在后面补上空格
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 3;
float b = 3.12345678;
double c = 3.12345678;
printf("%-5d!\n", a);
printf("%-8.4f!\n", b);
printf("%-7.3lf!\n", c);
return 0;
}
|
- %08.3f, 表示最小宽度为 8,保留 3 位小数,当宽度不足时在前面补上 0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 3;
float b = 3.12345678;
double c = 3.12345678;
printf("%05d\n", a);
printf("%08.4f\n", b);
printf("%07.3lf\n", c);
return 0;
}
|
if 语句
基本 if-else 语句
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cin >> a;
if (a > 5)
{
printf("%d is big!\n", a);
printf("%d + 1 = %d\n", a, a + 1);
}
else
{
printf("%d is small!\n", a);
printf("%d - 1 = %d\n", a, a - 1);
}
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cin >> a;
if (a > 5)
{
printf("%d is big!\n", a);
printf("%d + 1 = %d\n", a, a + 1);
}
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cin >> a;
if (a > 5)
printf("%d is big!\n", a);
else
printf("%d is small!\n", a);
return 0;
}
|
常用比较运算符
条件表达式
(1) 与 &&
(2) 或 ||
(3) 非 !